A Portable Inertial Navigation System for Total Hip Arthroplasty Targeting Direct Anterior Approach
Published in IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2025
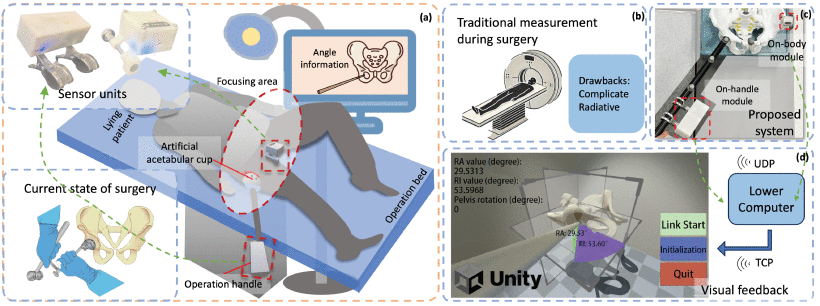
Abstract:
The past decade has witnessed the rise of total hip arthroplasty (THA) surgeries. Among all the approaches of THA, the minimally invasive Direct Anterior Approach (DAA) has gained significant interest in providing a faster recovery for patients. Precise acetabular prosthesis placement, particularly defined by the radiographic anteversion (RA) and radiographic inclination (RI) angles, is crucial for the success of DAA surgeries. However, conventional technologies such as computed tomography (CT) are costly and complex. This study presents a novel inertial measurement unit (IMU)-based navigation system to quantify these angles, especially for the DAA approach of THA. The system incorporates two sensor modules: one on-body module and one on-handle module. We comprehensively designed the hardware with circuitry and housing, and software including data transmission and visualization of the system. To evaluate the effectiveness, two sets of experiments were performed from both the sensor level and system level to assess the accuracy of the sensors and further validate the system under the condition of DAA. The system demonstrates validity with a root mean square error (RMSE) of 1.24° for RA and 1.89° for RI, alongside high reliability (CC larger than 0.995). The dynamic sensor drift is measured as less than 0.13°/min. Our system shows strong performance which is crucial in laying a solid foundation for future development. It demonstrates the potential for our system used in THA through DAA, and future work will focus on clinical trials to validate its efficacy in clinical settings.
Recommended citation: C. Gu et al., "A Portable Inertial Navigation System for Total Hip Arthroplasty Targeting Direct Anterior Approach," in
Download Paper
